
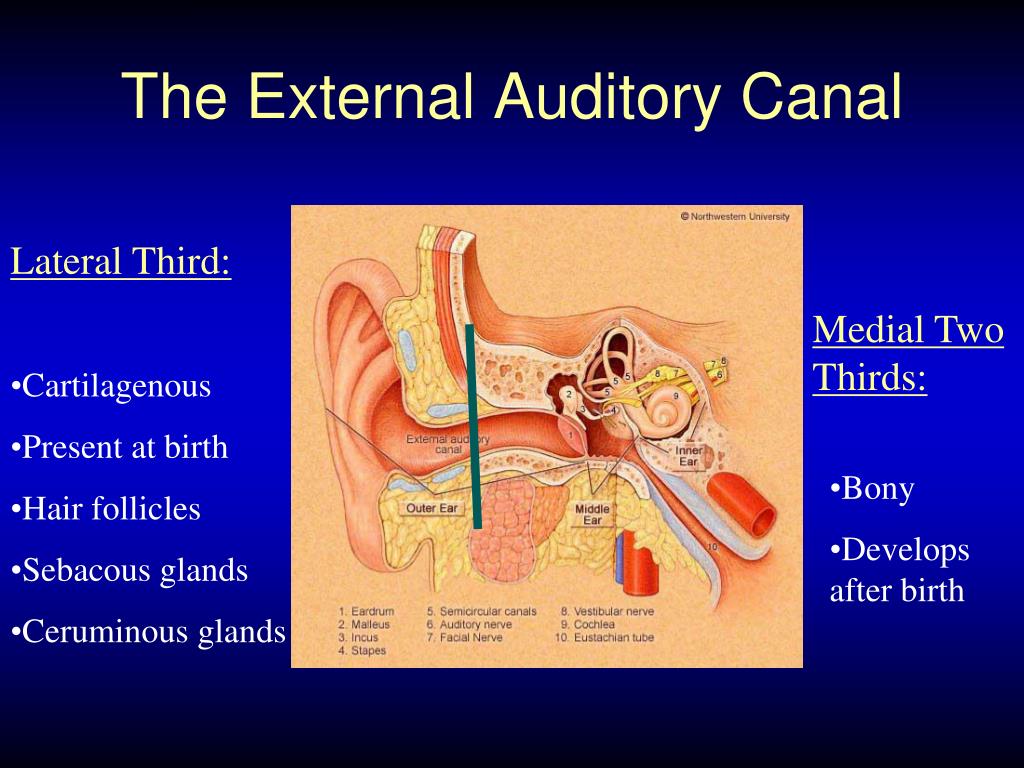
Without a microscope, a foreign body lying at or medial to the isthmus (the bony cartilaginous junction of the external auditory canal) is difficult to remove without injuring the delicate canal skin, tympanic membrane, or ossicular chain. Foreign bodies medial to the isthmus should be removed under operating microscope guidance by a specialist. If a smooth, rounded, or spherical foreign body is lateral to the isthmus (bony-cartilaginous junction), it should be removed by reaching behind the object and rolling it out. Patients with such objects should be referred to an otolaryngologist if the object cannot be easily removed with a curette. However, forceps tend to push round, smooth objects (eg, beads, beans) deeper into the canal. In general, foreign bodies that appear easy to grasp and remove (eg, paper, an insect wing) can be removed with alligator forceps by most practitioners. Symptoms include otalgia, often with systemic symptoms (eg, fever. It’s a hollow tube that curves slightly downward as it moves into the ear toward the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. read more and cause an acute otitis media Otitis Media (Acute) Acute otitis media is a bacterial or viral infection of the middle ear, usually accompanying an upper respiratory infection. In external ear atresia the external auditory canal is not developed and sound cannot reach the tympanic membrane. External acoustic meatus: This inch-long section is sometimes called the ear canal, and serves as the bridge between the outer and middle ear.

Symptoms include painless otorrhea with conductive hearing. Gently tug or jiggle your earlobe while tilting your head in a downward motion toward your shoulder. Water entering the middle ear through a tympanic membrane perforation may exacerbate chronic otitis media Otitis Media (Chronic Suppurative) Chronic suppurative otitis media is a persistent, chronically draining (> 6 weeks), suppurative perforation of the tympanic membrane. Jiggle your earlobe This first method may shake the water out of your ear right away. Irrigation is contraindicated in patients with a known tympanic membrane perforation or with a suspected infection. Irrigation may also be combined with cerumenolytic agents, such as liquid docusate sodium. Irrigation is often done in the emergency department or primary care setting and should be done carefully to avoid complications. These methods, particularly when done by an experienced practitioner, can be quicker and safer than irrigation. These keywords were added by machine and not by the. At the same time, earwax (cerumen) in the external auditory canal functions as a barrier to help keeping unwanted materials like dirt, dust, and insects out of the human ear. The stenosis of EAC is narrowing of the width of the EAC. Cerumen can be removed by rolling it out of the ear canal with a blunt curet or loop or a small, blunt right angle hook, or by removing it with a suction tip (eg, Baron, size 5 French). Parotid Gland Basal Cell Carcinoma Tympanic Membrane External Auditory Canal Chronic Otitis Medium. The external auditory canal (EAC) is formed by lateral cartila ginous and medial bony part.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
